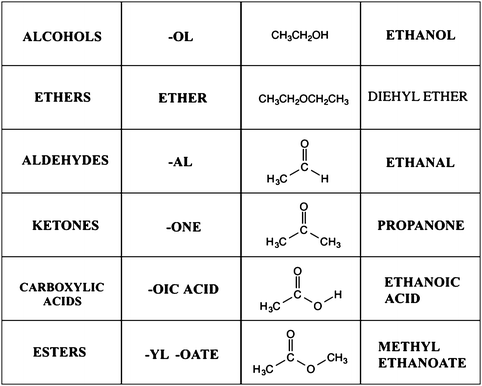
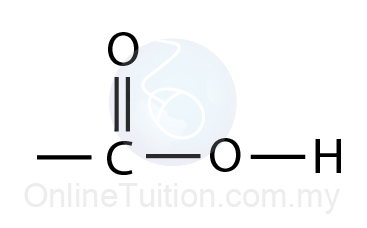
Functional group of carboxylic acid - Functional Groups
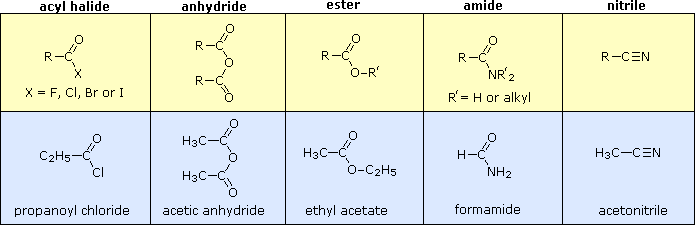
Nomenclature of Functional Groups: Order and Organic Compounds
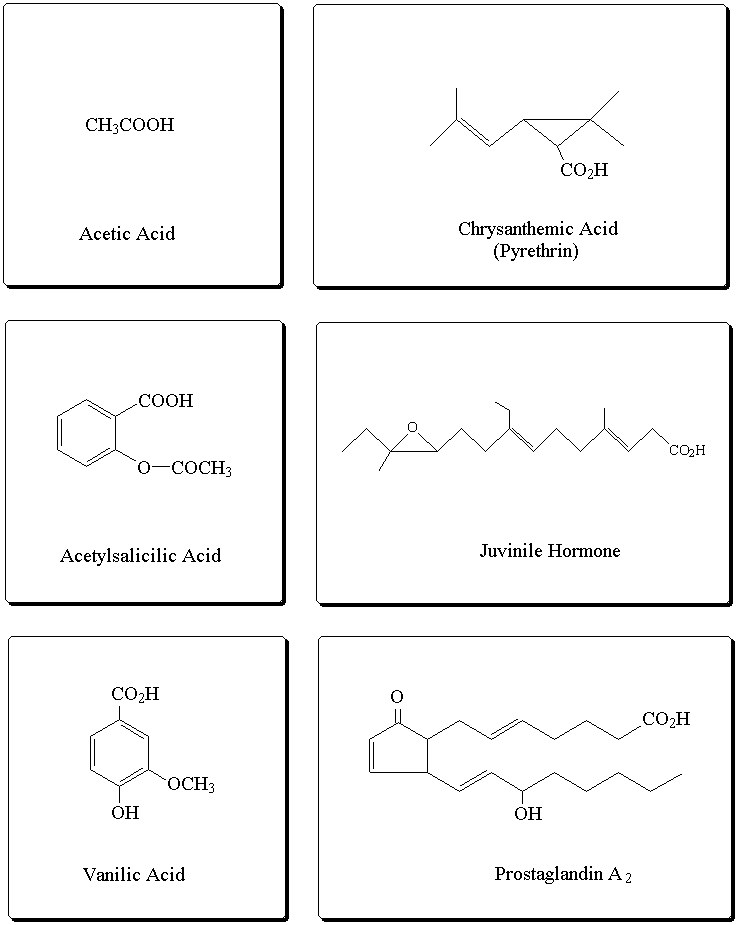
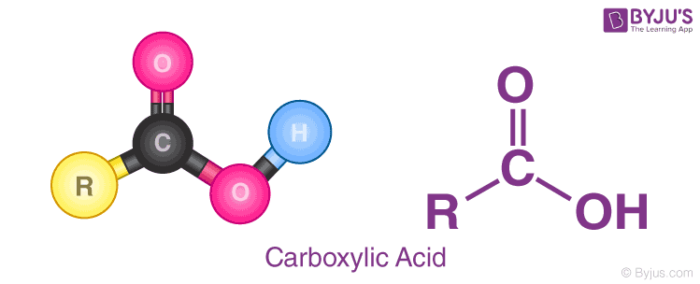
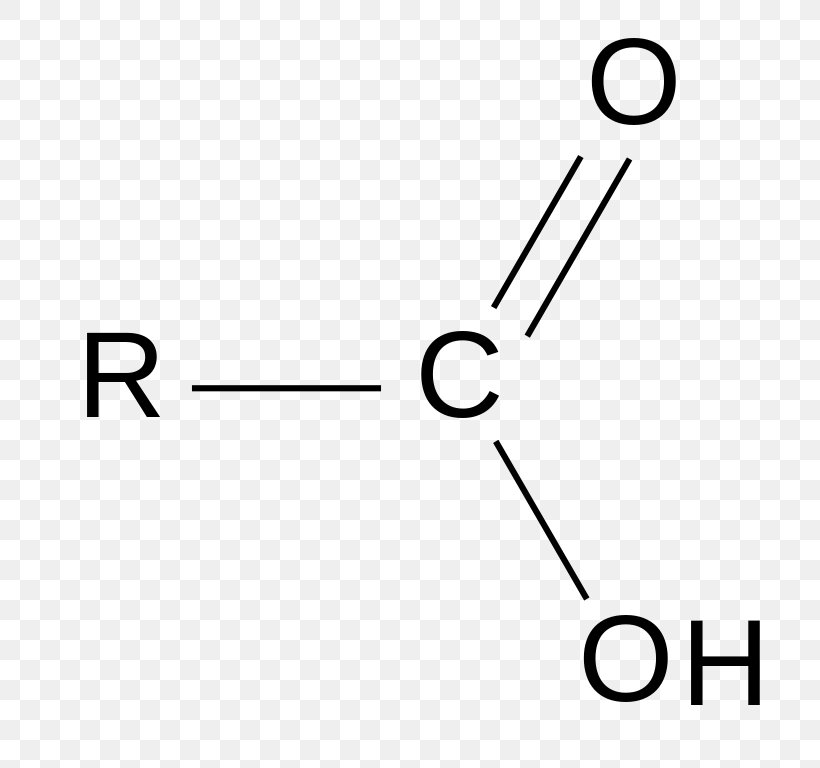
It is a typical group of functions shown in chemistry.
Reaction with ammonia Formation of amide : Carboxylic acids react with ammonia to form ammonium salt which on heating give amides.
Depending on the location of the carbonyl group, it is termed differently; ketones contain the carbonyl inside the compound and aldehydes contain the carbonyl at the end of the organic compound.
Carboxylic Acids: Structure, Examples, Formula, Test & Properties
It selectively activates the carboxylic acid to give the carboxymethyleneammonium salt, which can be reduced by a mild reductant like lithium tris t-butoxy aluminum hydride to afford an aldehyde in a one pot procedure.
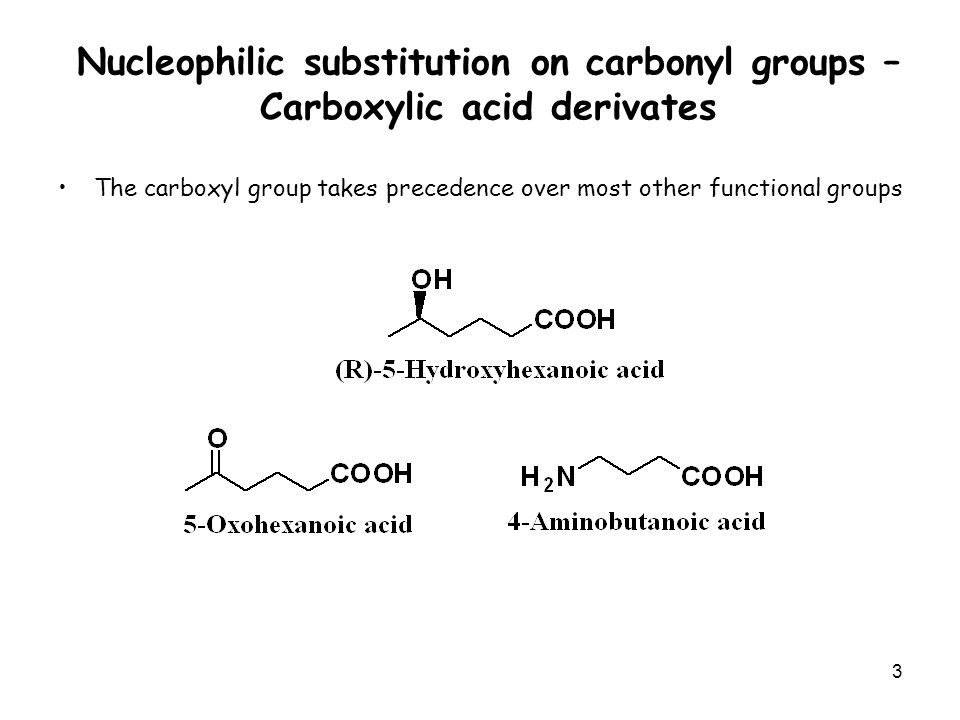
The newer method ranks the substituents for each C atom according to the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog sequence rules.
In an ester, the second oxygen atom bonds to another carbon atom.
- Related articles
2022 qa1.fuse.tv


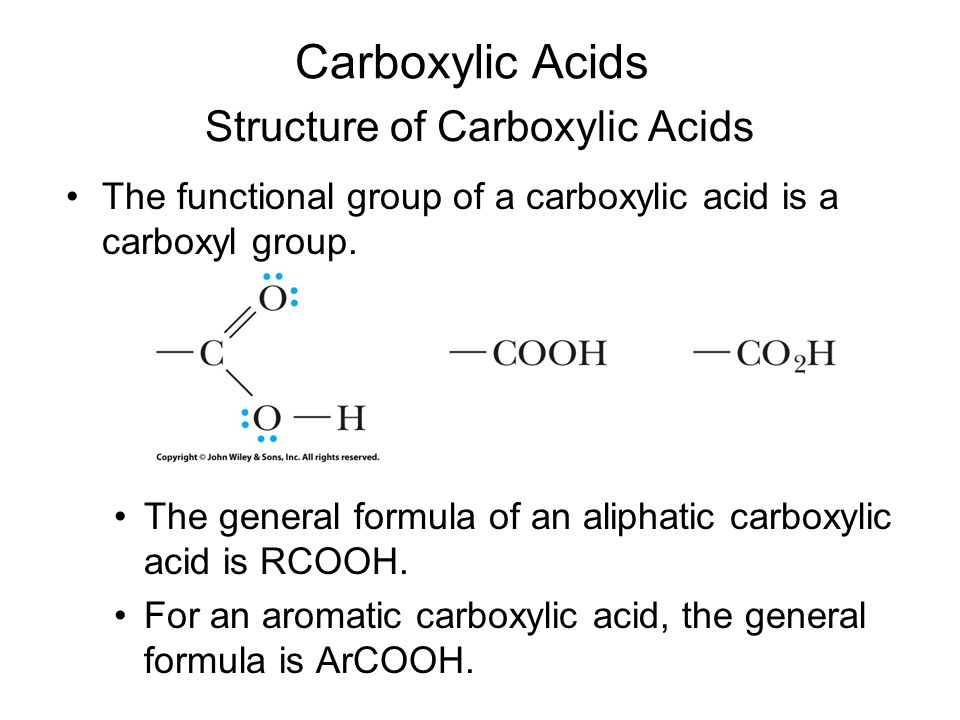






:strip_icc():format(jpeg)/kly-media-production/medias/1546381/original/015567400_1490342255-Surat-Cinta3.jpg)













)