Bacteria carrying a plasmid with an antibiotic resistance gene are important in cloning because - Plasmid and antibiotic resistance
Factors affecting plasmid production in Escherichia coli from a resource allocation standpoint
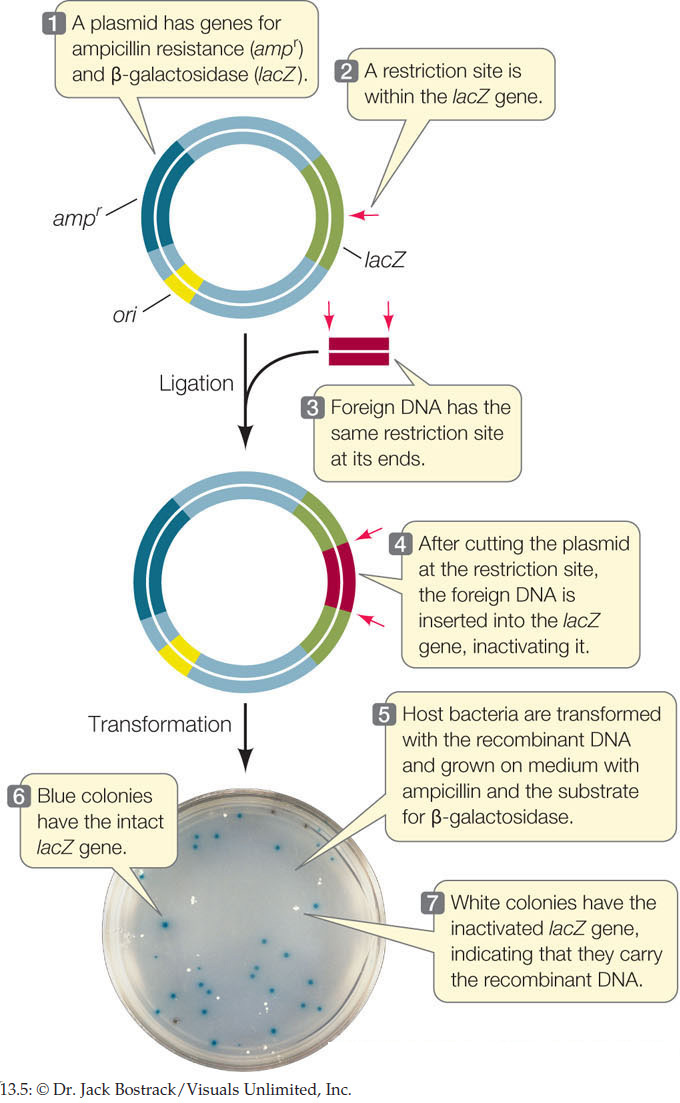
A piece of foreign DNA was inserted into a plasmid with an antibiotic resistance gene and lactose Z gene. The plasmid DNA was cut with a restriction enzyme, which splits the lactose Z gene and opens the circle. The foreign DNA was next inserted into the open restriction site of the plasmid. When the recombinant plasmid was introduced into bacterial cells and grown in the presence of antibiotic, some of the colonies turned blue in the presence of gene. The blue colonies contained
A Guide for Choosing Between Commonly Used Antibiotics
Chapter 9
Plasmids and co
A Guide for Choosing Between Commonly Used Antibiotics
Two different plasmids that belong to a similar family cannot co-exist in an identical cell.
Dna as well as a genetic marker for their selective recognition plasmids can involve! The structure of a plasmid is often double stranded and circular.
Ampicillin breaks down rather quickly so it is important to use ampicillin plates within four weeks for maximum activity.
- Related articles
2022 qa1.fuse.tv