Homeostasis - Homeostasis (Biology)
Recent Posts
- 羽生 结 弦 求婚 成功
- Video leak ebit lew
- Alopecia meaning
- Close contact sop malaysia 2022
- Milo 是 什么 国家 的
- Sai sakthi
- The quintessential quintuplets hentai
- Bazar ramadan near me
- Rosytime 价钱
- Kenny rogers sunway putra
- Video lunch korea
- Jumlah kes covid hari ini
- Israel new prime minister
- Waktu berbuka puasa johor bahru 2022
- Papa wolf and the puppy
10.7: Homeostasis and Feedback
Channel proteins are less selective than carrier proteins, and usually mildly discriminate between their cargo based on size and charge.
A vesicle is a membranous sac—a spherical and hollow organelle bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane.
The blood clotting cascade contains many zymogens.
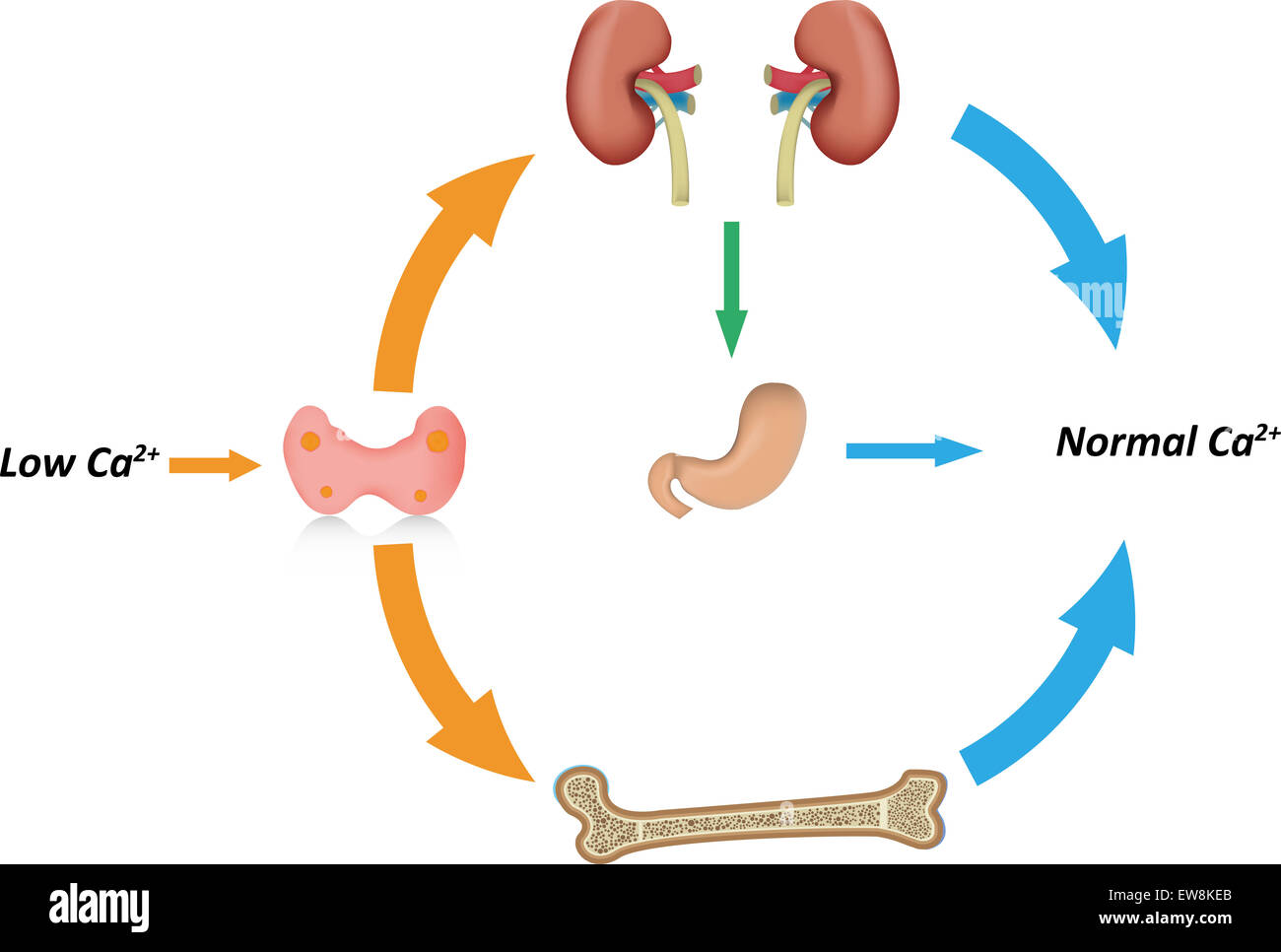
What Is Homeostasis?
Similarly, if an individual ate a lot of salty food, their body would work to keep their internal salinity at a safe parameter by filtering out unneeded salts.
The body must maintain proper glucose levels to ensure a person remains healthy.
If blood glucose levels drop too low, the liver converts in the blood to glucose again, raising the levels.
- Related articles
2022 qa1.fuse.tv





















/pixlr-e-editor-c17451ffb95344c5918221a240934613.png)




